Defining Default Imaging Settings
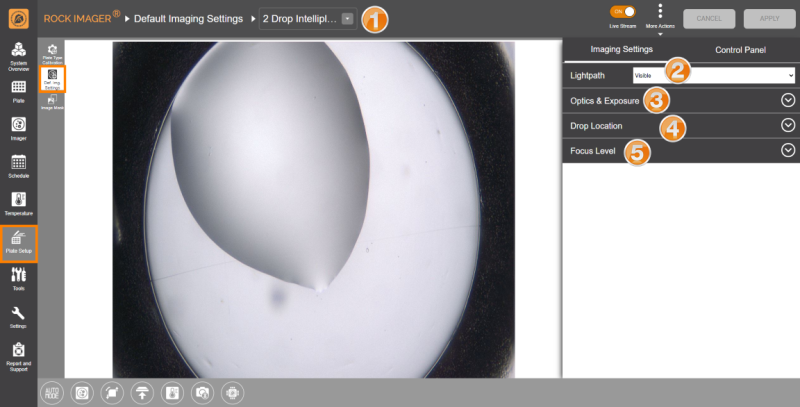
The Default Imaging Settings sub-menu is where you define the default optics and camera settings to use when imaging a certain plate type.
Upon installation, the FORMULATRIX support team will configure the properties for optimal image quality and performance. If you need to add a new plate type to your imager, then please contact support@formulatrix.com for help. We recommend that only advanced users modify these settings. The information below is for lab managers so that they may adjust settings as they see fit.
Note: The Control Panel is available next to the Imaging Settings panel so you can easily navigate between the wells, zoom in and out of the drops, and adjust the camera and optics settings without having to go to the Imager menu.
Item | Description |
 Plate Type List | Select the plate type you are interested in editing. You can add new plate types to the list from ROCK MAKER software. You can export new plate type definitions by clicking More Actions and selecting Export. The system will save your plate type settings in an .XML file format. You can also use the Import feature to import the file later if needed or if you obtain new plate type settings from FORMULATRIX support. |
 Lightpath | Select the lightpath of interest. The type of imaging modes available here depends on the imaging types you purchased. The Visible lightpath is the default imaging setting and is always present. Each lightpath provides slightly different settings for area numbers 3, 4, and 5. If you select Ultraviolet, the Enable For This Plate Type option will show up. Enabling this option allows you to image your experiments using UV lightpath. |
 Optics and Exposure | This area contains settings for the optics components and resolutions along with the exposure settings to use during plate imaging.  Optics & Exposure Options for Visible Lightpath  Optics & Exposure Options for Ultraviolet Lightpath
Note: The exposure settings for each drop can be different depending on the conditions of each drop. |
 Drop Location | Drop Location settings determine how ROCK IMAGER® executes the Drop Location algorithm for the selected plate type. Options may vary depending on the imaging methods you purchased.  Drop Location Options for Visible Lightpath  Drop Location Options for Ultraviolet Lightpath ROCK IMAGER® can execute Drop Location in two ways: Fixed method and Locate Drop method.
Selecting Fixed tells ROCK IMAGER® to use the drop positions defined in the Drop Positions panel when imaging an experiment. If the selected plate type has more than one drop per well, you can instruct the system to image each drop on the well using different zoom settings by selecting the Override Zoom check box.  Override Zoom Option
This method instructs ROCK IMAGER® to run the Locate Drop algorithm before capturing images. Before imaging, the system will perform an overview using the zoom value defined in the Zoom box and the objective (for UV lightpath) from the Objective list. The system will find a drop location using these exact settings. Note: The Objective and Zoom options are only available if your hardware supports continuous zoom or objective lenses.
Locate Drop Method Settings When using the Locate Drop method, you can further customize how to run the Drop Location algorithm.  Locate Drop Method Settings From the Method box, you can choose between Standard and Lipidic Cubic Phase (LCP). The LCP method instructs ROCK IMAGER® on how to locate drops on an LCP or glass plate. The other fields determine the optics and camera settings used while the system is locating a drop before imaging. Advanced Settings Option for Standard Method
|
 Focus Level | Think of Focus Level as a capture range. These settings dictate how the system images a drop once it locates one and adjust the number of focus levels acquired. You can select Auto Focus with Limits, Fixed Range (DoF Limited), or Fixed Range (Interpolated). Auto Focus with Limits Runs the Auto Focus algorithm on the drop to pinpoint the best focus level for the drop on the Z axis. Once the focus level is determined, the system captures images above and below this point, called “slices”. The slices are analyzed and compiled by ROCK IMAGER Processor into Extended Focus Image (EFI), which is the default image displayed in ROCK MAKER. Note: Auto Focus with Limits is used when the Z position of the drop is inconsistent across the plate. This can be used for LCP and hanging drop experiments.  Auto Focus with Limits There are five settings that dictate how slices are acquired:
Note: While acquiring too many focus levels will increase the drop details, it will also result in a longer imaging time.
Using this option, ROCK IMAGER® will capture slices along the Z axis between the start and stop heights and also determine the best number of slices to take based on the Depth of Field (DOF) of the optics in use.  Fixed Range (DoF Limited)
Using this setting, ROCK IMAGER® will capture slices along the start and stop z-heights of the drop. You will need to type the desired focus levels to be acquired in the Focus Levels box.  Fixed Range (Interpolated) Capture Levels
Available for Visible light path only. This setting limits the movement of Auto Focus (in mm) with the default values for the Auto Focus Range between 0 - 0.5 mm. You can change these values by typing your desired values into the corresponding boxes. |
FORMULATRIX® is proudly powered by WordPress